
Senior writer Tina Hesman Saey is a geneticist-turned-science writer who covers all things microscopic and a few too big to be viewed under a microscope. She is an honors graduate of the University of Nebraska-Lincoln where she did research on tobacco plants and ethanol-producing bacteria. She spent a year as a Fulbright scholar at the Georg-August University in Göttingen, Germany, studying microbiology and traveling. Her work on how yeast turn on and off one gene earned her a Ph.D. in molecular genetics at Washington University in St. Louis. Tina then rounded out her degree collection with a master’s in science journalism from Boston University. She interned at the Dallas Morning News and Science News before returning to St. Louis to cover biotechnology, genetics and medical science for the St. Louis Post-Dispatch. After a seven year stint as a newspaper reporter, she returned to Science News. Her work has been honored by the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering and Medicine, the Endocrine Society, the Genetics Society of America and by journalism organizations.

Trustworthy journalism comes at a price.
Scientists and journalists share a core belief in questioning, observing and verifying to reach the truth. Science News reports on crucial research and discovery across science disciplines. We need your financial support to make it happen – every contribution makes a difference.
All Stories by Tina Hesman Saey
-
 Genetics
GeneticsWho decides whether to use gene drives against malaria-carrying mosquitoes?
As CRISPR-based gene drives to eliminate malaria-carrying mosquitoes pass new tests, the African public will weigh in on whether to unleash them.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineTrained dogs sniff out COVID-19 as well as lab tests do
Dogs can be trained to sniff out COVID-19 cases. They’re overall as reliable as PCR tests and even better at IDing asymptomatic cases, a study suggests.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & Medicine4 answers to key questions about the monkeypox outbreak
Monkeypox has cropped up around the world, but it doesn’t spread easily like the coronavirus and most people probably don’t need to be concerned.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHere’s the latest good and bad news about COVID-19 drugs
After coronavirus vaccines, antivirals and a monoclonal antibody are the next line of defense, but the treatments may be hard for some people to find.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThe body’s response to allergic asthma also helps protect against COVID-19
A protein called IL-13 mounts defenses that include virus-trapping mucus and armor that shields airway cells from infection.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHow I decided on a second COVID-19 booster shot
Boosters help for a short time, and mixing vaccines doesn’t seem to push the immune system toward making unhelpful antibodies, studies show.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsWe finally have a fully complete human genome
Finding the missing 8 percent of the human genome gives researchers a more powerful tool to better understand human health, disease and evolution.
-
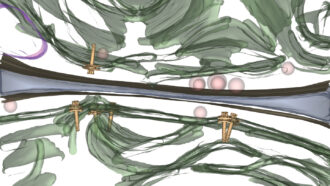 Microbes
MicrobesNew images reveal details of two bacteria’s molecular syringes
It’s unclear exactly how these species use their tiny injectors, but learning how they work could lead to nanodevices that target specific bacteria.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHow I’ll decide when it’s time to ditch my mask
New COVID-19 masking guidelines are designed for communities not individuals, making a decision about safety difficult.
-
 Life
LifeSome E. coli set off viral grenades inside nearby bacteria
A bacterial toxin called colibactin awakens dormant viruses embedded in bacterial DNA, but its ecological role is still unknown.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHow to interpret the CDC’s new mask guidelines
Based on the CDC’s new metrics, most people no longer need to wear masks in most situations, but that could change.
-
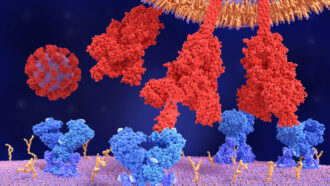 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHow omicron’s mutations make it the most infectious coronavirus variant yet
With its mishmash of mutations, omicron has a unique anatomy that has helped fuel its dominance.